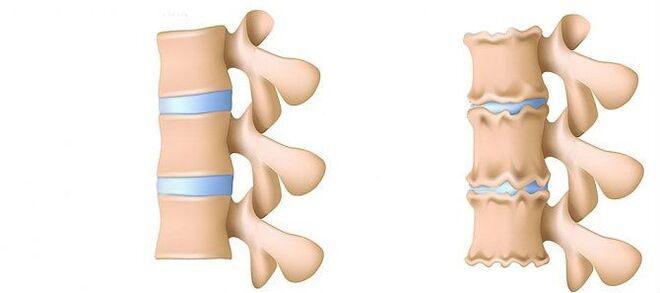
The osteochondrosis of the lumbar region is a disease that deforms and destroys the cartilaginous tissue of the intervertebral discs in the lower back.Without cartilage layer, the distance between the vertebrae is significantly reduced.And with the slightest turns, they can change.The main danger of disease is the possibility of intervertebral hernia formation.
Can't you bow to lift an object that has fallen to the floor?Do you suffer acute pain in the lumbar column and often go, wrapping the waist in a warm scarf?Do not ignore the condition that bothers you.
Osteochondrosis of the lumbar region can be dragged by its duration for a long time.There is no need to experience the body for force.Love your body.And it will correspond.
The lumbar region represents most of the load of all body weight compared to the thorax and cervical departments.Therefore, this subspecies of osteochondrosis is the most common.
What are the stages of development of osteochondrosis?
- First stage.PreclinedThe height of the disc is reduced.In the fibrous ring (the outer layer of the intervertebral disk of the cartilaginous fibers) a crack is formed.Lumbar muscles begin to get tired quickly.You feel safe discomfort in the back.
- Stage 2. Violations of metabolic processes in the core jacket (central part of the intervertebral disc, which consists of a cartilage jacket): their cells are dead or completely destroyed.The collagen structure (the structure of the protein is based on the connective tissue) of the fibrous ring is also altered.Local Dolores, a person cannot deal with physical activity that he previously considered quite feasible.
- Stage 3. Complete destruction of the fibrous ring.The adjacent vertebrae cease to be stable.Any uncomfortable cause causes pain.Due to the experience of nerve roots that move away from the spinal cord, the limbs can become less sensitive and mobile.
- 4th stage.The intervertebral disc fabrics become scars.The vertebra can result in the housing housing.The clinical description here depends on individual physiology.
Lumbar pain (lumbago) and the pain that gives the leg during the sciatic nerve (Ishias) is one of the most common complaints that patients seek medical help.Due to the fact that these symptoms are quite common in the general population, and their constant growth, diagnosis and treatment of such patients will continue to be one of the main areas of activity of neurosurgical hospitals.Despite the extension of this pathology, the surgical elimination of the hernia of the intervertebral disc (MPD) is required only in 10% of patients with the clinical image of lumbar algia.In the remaining part of the patients, the best effect has a conservative treatment, which includes drug therapy, physiotherapy exercises, the use of physiotherapeutic treatment methods, as well as a return to previous daily physical activity.
Stages of the disease
Degenerative discrete processes often begin with a deterioration in the intervertebral disc absorption function.
- Deterioration of the blood supply to the intervertebral disc.In adults, the food of the intervertebral discs is carried out by diffusion: the blood is administered only to the vertebrae, and already through them "filters" the discs.In the best way, the disc is fed during dynamic loads (for example, walking), since the principle of the pump (output of the processed fluid when compressed, the flow of nutrients and oxygen by eliminating the load).Therefore, the nutrition of intervertebral discs is difficult, especially in the conditions of a sedentary lifestyle (hypodinamia).
- Changes in the nucleus of the pulp disc.With a deterioration in the blood supply, the water supply, sugars and amino acids to the octopus nucleus is altered.Because of this, the production of carbohydrates that connect water suffers.The nucleus is dehydrated, its structure made of gel becomes fibrous, the ability to sprout and extinguish the shots worsen.This increases the load in the fibrous ring and the vertebrae, they are more likely to be blocked and injured.
- Changes in the fibrous ring of the intervertebral disc.Due to the flattening of the octopoose nucleus, the increase in the load is found in the fibrous disk ring.In conditions of poor blood supply, the fibrous ring loses its resistance.The instability of the column occurs, which can lead to the formation of an intervertebral hernia, a displacement of the vertebrae and the damage to the spinal cord or the nerve roots.
- Disk profusion.The formation of intervertebral hernia.As the fibrous ring fibers weaken, the pulpic nucleus begins to excel, for example, towards the intervertebral channel (disc protuberance).Such amazing can lead to a rupture of a fibrous ring and the formation of a hernia.Read more about the intervertebral hernia formation process in a separate article: "Effective treatment of intervertebral hernia in the home".
- Spondylosis is the destruction of intervertebral joints (spondilartrosis), the growth of osteofites and ligament ossification.Parallel to the formation of intervertebral hernia in the osteochondrosis, damage to the intervertebral joints are observed, destructive changes in the vertebra (cartilage) and ligaments are observed.
As the osteochondrosis and the development of complications advance, it must resort to medications increasingly often the dose.This leads to high financial costs, as well as a greater deterioration of health due to the side effects of medicines.
Pharmacological therapy, as a rule, is complemented by the immobilization of one or friend of the column using orthopedic corsets of various degrees of rigidity.
The surgical treatment is justified only in cases where the level of compression of the spinal tower, determined by the clinic, corresponds to the exam that confirms the rupture of the fibrous ring with the "loss" of the hernia of the MPD in the light of the vertebral channel [3–6].The results of the surgical treatment in patients with small bumps of the disk, as a rule, are disappointed with doctors and the patient himself.The method to establish a precise diagnosis is magnetic resonance (MRI).Approximately 10% of people in a common population is impossible to perform a magnetic resonance of routine due to claustrophobia (fear of closed spaces).However, in this category of people, it is possible to use the "open" magnetic resonance of SO with the corresponding loss of quality of the images obtained.Patients who have previously suffered surgical treatment should carry out a magnetic resonance with contrasting reinforcement to delimit postoperative scar changes the true hernial protuberance of the disc.In patients with suspected hernial protuberance of the MPD, when the implementation of magnetic resonance is impossible, or the results obtained are not very informative, the tomographic myelography (CT) acquires a special diagnostic value.
Private diagnostic specialists who interpret the results of the studies, as a rule, exaggerate the degree of damage to the disk due to the impossibility of comparing clinical data with "findings" during tomography.Conclusions such as "changes correspond to the patient's age" are almost never found in research protocols.Despite the improvement of neuroimaging techniques, the responsibility of the correctly deceived diagnosis is found on the clinician's shoulders, since only he can compare the clinical image with the data obtained during tomography.An increase in tomograph resolution improved the results of slightly improved surgical treatment, but deviations from the norm in asymptomatic patients began to be detected.The process of processes that accompany the degenerative lesion -Distritical of the column have suffered serious progress in recent years.The arthropathy ofArchaehed joints is widespread in the general population and is detected quite often in people of the Middle and higher age group during TC investigation. Degenerative changes in MPD, which are also widely used, are often detected quite frequently, and magnetic resonance is a more specific method for diagnosis.At the same time, the changes pronounced in the MPD are not uncommon, not accompanied by a rupture of the fibrous ring, but are only manifested by a slight "stab" of the album in the light of the spinal canal or the intervertebral holes.In some cases, the degenerative processes that occur in the MPD can lead to the destruction of the fibrous ring with later ruptures, which causes migration from the pulpal nucleus outside the disc with compression of the adjacent roots of the spinal cord.The statement that if pain is observed in the leg, then it must necessarily violate the spinal cord roots is not entirely true.To the pain in the buttock with irradiation on the posterior surface of the thigh can lead both the degeneration of the MPD and the arched intervertebral joints.For a true ishyalgia attack caused by the compression of the koreshka of the Hernia MPD nerve, the pain radiates on the posterior surface of the thigh and the lower part of the leg.AIndefinite pain, limited only to the gluteal area or the area of the thigh without distribution along the sciatic nerve, as well as bilateral pain in the gluteal areas or hips that change their location (either to the right, then to the left), are caused more frequently by the arthropathy of the arched joints or the diffuse degeneration of the MPD.The clinical image of the Koruska compression of the MPD hernia can also be a concomitant pathology (for example, osteoarthritis of the knee joints).In patients with such pain, the surgical treatment will not have the proper effect, regardless of which pathology it will be detected by the tomographic exam.In other words, in patients only with the pain clinic on the back, the elimination of the MPD hernia will be ineffective, even if the volumes are determined by the protuberance of the MPD, as usual and happens.But there are also patients in which the typical Ishias image is accompanied by a pronounced disabled pain syndrome, while during studies performed using highly perceptual tomographs, the compression of the spinal cord roots is not determined.This category of patients is inappropriate to perform surgical intervention, since over time, root symptoms, as a rule, decrease.
It is necessary to clearly imagine the mechanisms that lead to the development of MPD hernial protuberance to recommend to patients the volume of allowed movements, not forgetting work activity.Forces that contribute to the formation of hernial protuberance are the result of degenerative changes in the MPD and a decrease in the vertical (height) of both the fibrous ring and the octopoose nucleus.The MPD stabbing fragment in 80% changes in the posterior direction of the beard, while entering the spinal canal and the medial sections of the intervertebral hole.This displacement of the MPD hernia towards the midline is facilitated by the retention force of the posterior longitudinal ligament.Up to 10% of the herns are located laterally and extend to the intervertebral hole (Hernias Forsin) or on the outer edge of the hole where the cephalorrajía column comes out, pressing it.
In the vital activity process, dehydration and degenerative changes lead to the loss of MPD height.These pathological processes involve both a fibrous ring and a pulpal nucleus.The most pronounced destruction of the octopo nucleus in the context of the concomitant degeneration of the fibrous ring, as a rule, only leads to the loss of the MPD height without its significant meetings.With the predominant changes in the fibrous ring, the vertical forces that affect the preserved pulpal nucleus and that are a derivative of their own weight, as well as the muscles of the back, which act on the disc in the lateral direction, exerts excess pressure in the remaining fragment of the octopoose nucleus, which cannot retain the fibrous ring in its place.
The sum of these two forces leads to an increase in centrifugal pressure in the MPD, which, together with the stretching component that acts on the fibrous ring fiber, can lead to its rupture and fragment of fragments of the remaining pulp nucleus.After a hernial protuberance was formed, and the "redundant" fragment of the pulpal nucleus was out of the fibrous ring, the MPD structure is again stable [2].As a result of the forces that affect the degeneratively altered nucleus and the fibrous ring of the MPD, they are balanced, and its vector, which contributes to a greater protuberance of fragments of the nucleus, fades.In some cases, partial degenerative changes in the pulp nucleus contribute to gas formation within the MPD, followed by excessive pressure in its remaining fragment.The formation of a hernia is also accompanied by the gas formation process within the disc.
The excessive and acute physical activity shown in the patient's back, at the bottom of the degenerative lesion -Distophical of the column, is usually only a trigger that leads to a detailed clinical image of a root compression syndrome, which is often considered by the patients themselves, such as the worldwide lumbar -icialgia.Clinically, MPD hernia can manifest with reflex and compression syndromes.The syndromes are referred to compression, in which the anterior hernial protuberance is extracted, squeezed, squeezed and deorted, the blood vessels or the spinal cord are compressed and deform.Reflex reflexes include syndromes caused by the effects of disc hernia on the receptors of these structures, mainly the end of the spinal nerves of return, which leads to the development of reflex and tonic disorders manifested by vasomotor, dystropic and myofascial disorders.
As noted above, surgical treatment with degenerative lesion -postvinor's diastrophic is advisable only in 10% of patients, the remaining 90% react well to conservative measures.The basic principles of using the latter are:
- Pain relief;
- Restoration of the correct posture to maintain the fixation capacity of the changed MPD;
- elimination of muscle and tonic disorders;
- Restoration of blood circulation in roots and spinal cord;
- Standardization of conductivity in nerve fiber;
- elimination of scar and spaced changes;
- Relocation of psychoconsomatic disorders.
Treatment
Today, in the treatment of osteochondrosis and its complications, medications of the following groups are used:
- Net -re anti -inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): in the form of drugs or drug injections.These funds have the ability to reduce pain, reduce inflammation activity.However, the effect of its use does not last long, from several hours to two to three days.Therefore, such funds must be taken for a long time, weeks and sometimes months.At the same time, these drugs negatively affect the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract.Its long -term reception is loaded with the development of gastritis, ulcer lesions.In addition, they can negatively affect the work of the kidneys, the liver and contribute to the development of hypertension.And, at the same time, these funds do not contribute to the cleaning of dead cell discs.Therefore, its use is only a way to relieve symptoms for a while, but not eliminate the main problem.
- CTEPOID (GOPMONAL) Anti -inflammatory drugs.As a general rule, they are used for severe and impenetrable pains that accompany hernia, radiculitis, ishias, etc.Gopmons have the ability to eliminate inflammation manifestations (due to the oppression of the immune system), relieve pain.But they also negatively affect the mucous membranes of the stomach and the intestine, promote the leaching of the calcium of the bones, inhibit the production of their own Gopmons.And do not contribute to clean the focus of dead cells.
- Potatoes are drugs that affect the muscles or nerves that go to the muscles and cause relaxation of the skeletal muscles.These media help relieve muscle clamps for a while, reduce pain and improve blood flow.But at the same time, they do not help clean the tissue of dead cells.Therefore, they do not contribute to the cure for osteochondrosis.
- Epidupal block: the introduction of analgesics and gopmonal agents in the space between the solid brain cover and the periosteum that covers the vertebrae.It is used, as a rule, for intense pain: in the acute period of intervertebral hernia, with severe radiculitis, Ishias.Depending on the composition, this injection helps relieve pain for a period of several hours to several days.After the expiration date, manifestations of the disease are returned, because the procedure does not help restore metabolic processes on the discs.In addition, when it is carried out, there is a risk of lesions in blood vessels and nerves.
Conservative treatment methods include various orthopedic effects in the spine (corset immobilization, traction, manual therapy), physiotherapy (therapeutic massage, physiotherapy exercises, acupuncture, electrotherapy, spots, various types of heating), paravertebral, peridural block and medication.The treatment of the degenerative injury -Distophical of the column must be complex and in phase.As a general rule, the general principle of conservative measures is the appointment of analgesics, non -steroid anti -inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), muscle relaxants and physiotherapy.
The analgesic effect is achieved by appointing diclofenac, ketoprofen, lornoxicam, tramadol.A pronounced analgesic and anti -inflammatory effect has paroxas, existing in forms of injection and tablet.
NSAIDs are the most used drugs for degenerative damage -distributing of the spine.They have an anti -inflammatory, analgesic and antipyretic effect associated with the suppression of the cyclooxygenase enzyme (COC -1 and Tsos -2), which regulates the transformation of arachidonic acid in prostaglandins, prostacillas, thromboxes.In the elderly and patients with risk factors for side effects, it is advisable to carry out the "coverage" of gastrooterctor under "coverage."In such patients, when completing the course of NSAID injection therapy, the transition to the Tablet forms of CO -2 inhibitors, which have a lower gravity of the side effects of the gastrointestinal tract.
To eliminate pain associated with the increase in muscle tone, it is advisable to include central muscles in complex therapy.
The surgical treatment of the degenerative lesion -Distophical of the column is justified with the inefficiency of complex conservative measures (within 2-3 weeks) in patients with MPD hernias (usually more than 10 mm) and not possible root symptoms.There are emergency indications for surgical intervention with a "fall" kidnapping in the light of the spinal channel and the expressed compression of the spinal cord roots.The development of the flow syndrome is facilitated by acute radiculomilohemia, which leads to a severe hyperalgic syndrome, when even the prescription of drug traffickers, the use of blocking (with glucocorticoid and anesthetic) does not reduce the severity of pain.It is important to keep in mind that the absolute size of the album hernia does not have a determining value to make the final decision on the surgical intervention and should be considered in relation to the clinical picture and the findings detected by the tomographic exam.In 95% of cases, open access to the vertebral channel is used in hernia.Several decoupling techniques (cold plasma coagulation, laser reconstruction, etc.) were not currently not performed today, and their use is only justified only for MPD bumps.The classic open micro -surgical elimination of the hernia of the disk is carried out using micro -surgical tools, binocular magnifiers or an operating microscope.Analysis of distant treatment results (Within More than 2 Years) 13,359 patients Who Underwent the Removal of the Mpd Hernia, 6135 of which the sequestral was removed, and 7224 Aggressive discsctomy was Carried Out, Showed that the relapse of pain Was Found 2.5 TimesMore Ophtan (27.8% versus 11.6%) in patients who have moved attribute the discoctomy, While relapse of hernias was notted 2 times more likely (7% versus 3.5%) in patients who only eliminated kidnapping.The quality of life is reduced more in patients who experience pain syndrome, while repeated hernia formation is not always clinically manifested.
In conclusion, once again it would emphasize the need for an exhaustive clinical examination and the analysis of the volumes to make an optimal decision on the choice of tactics for the treatment of a particular patient.















